容器概觀
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext 介面代表 Spring IoC 容器,並負責實例化、組態和組裝 bean。容器透過讀取組態中繼資料,取得關於要實例化、組態和組裝的組件的指示。組態中繼資料可以表示為註解組件類別、具有工廠方法的組態類別,或外部 XML 檔案或 Groovy 腳本。無論使用哪種格式,您都可以組合您的應用程式以及這些組件之間豐富的相互依賴關係。
ApplicationContext 介面的幾個實作是 Spring 核心的一部分。在獨立應用程式中,通常會建立 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 或 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的實例。
在大多數應用程式情境中,不需要顯式的使用者程式碼來實例化一個或多個 Spring IoC 容器的實例。例如,在純粹的 Web 應用程式情境中,應用程式的 web.xml 檔案中的簡單樣板 Web 描述器 XML 就足夠了(請參閱 Web 應用程式的便捷 ApplicationContext 實例化)。在 Spring Boot 情境中,應用程式 Context 會根據常見的設定慣例隱式地為您啟動。
下圖顯示 Spring 如何運作的高階視圖。您的應用程式類別與組態中繼資料結合,以便在建立和初始化 ApplicationContext 後,您擁有一個完全組態且可執行的系統或應用程式。
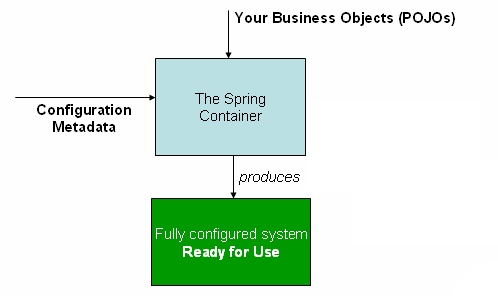
組態中繼資料
如上圖所示,Spring IoC 容器會使用一種組態中繼資料。此組態中繼資料表示您作為應用程式開發人員,如何告訴 Spring 容器實例化、組態和組裝應用程式中的組件。
Spring IoC 容器本身與實際編寫此組態中繼資料的格式完全解耦。現在,許多開發人員為他們的 Spring 應用程式選擇 基於 Java 的組態
-
基於註解的組態:在應用程式的組件類別上使用基於註解的組態中繼資料來定義 bean。
-
基於 Java 的組態:透過使用基於 Java 的組態類別,在應用程式類別外部定義 bean。要使用這些功能,請參閱
@Configuration、@Bean、@Import和@DependsOn註解。
Spring 組態至少包含一個,通常多個容器必須管理的 bean 定義。Java 組態通常在 @Configuration 類別中使用 @Bean 註解的方法,每個方法對應一個 bean 定義。
這些 bean 定義對應於構成您應用程式的實際物件。通常,您會定義服務層物件、持久層物件(例如儲存庫或資料存取物件 (DAO))、呈現物件(例如 Web 控制器)、基礎架構物件(例如 JPA EntityManagerFactory)、JMS 佇列等等。通常,不會在容器中組態細粒度的網域物件,因為建立和載入網域物件通常是儲存庫和業務邏輯的責任。
XML 作為外部組態 DSL
基於 XML 的組態中繼資料將這些 bean 組態為頂層 <beans/> 元素內的 <bean/> 元素。以下範例顯示基於 XML 的組態中繼資料的基本結構
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="..." class="..."> (1) (2)
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="..." class="...">
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions go here -->
</beans>| 1 | id 屬性是一個字串,用於識別個別的 bean 定義。 |
| 2 | class 屬性定義 bean 的類型,並使用完整類別名稱。 |
id 屬性的值可用於參考協作物件。此範例中未顯示用於參考協作物件的 XML。有關更多資訊,請參閱 相依性。
為了實例化容器,需要將 XML 資源檔案的位置路徑提供給 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 建構子,以便容器從各種外部資源(例如本機檔案系統、Java CLASSPATH 等)載入組態中繼資料。
-
Java
-
Kotlin
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");val context = ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml")|
在您了解 Spring 的 IoC 容器之後,您可能想要了解更多關於 Spring 的 |
以下範例顯示服務層物件 (services.xml) 組態檔
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- services -->
<bean id="petStore" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.services.PetStoreServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
<property name="itemDao" ref="itemDao"/>
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions for services go here -->
</beans>以下範例顯示資料存取物件 daos.xml 檔案
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountDao"
class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.dao.jpa.JpaAccountDao">
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="itemDao" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.dao.jpa.JpaItemDao">
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions for data access objects go here -->
</beans>在前面的範例中,服務層由 PetStoreServiceImpl 類別和兩種資料存取物件類型 JpaAccountDao 和 JpaItemDao(基於 JPA 物件關聯對應標準)組成。property name 元素參考 JavaBean 屬性的名稱,而 ref 元素參考另一個 bean 定義的名稱。id 和 ref 元素之間的這種連結表達了協作物件之間的相依性。有關組態物件相依性的詳細資訊,請參閱 相依性。
組合基於 XML 的組態中繼資料
將 bean 定義分散在多個 XML 檔案中可能很有用。通常,每個個別的 XML 組態檔案代表您架構中的邏輯層或模組。
您可以使用 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 建構子從 XML 片段載入 bean 定義。此建構子接受多個 Resource 位置,如 前一節 所示。或者,使用一個或多個 <import/> 元素從另一個檔案或多個檔案載入 bean 定義。以下範例顯示如何執行此操作
<beans>
<import resource="services.xml"/>
<import resource="resources/messageSource.xml"/>
<import resource="/resources/themeSource.xml"/>
<bean id="bean1" class="..."/>
<bean id="bean2" class="..."/>
</beans>在前面的範例中,外部 bean 定義是從三個檔案載入的:services.xml、messageSource.xml 和 themeSource.xml。所有位置路徑都相對於執行匯入的定義檔案,因此 services.xml 必須與執行匯入的檔案位於相同的目錄或類別路徑位置,而 messageSource.xml 和 themeSource.xml 必須位於匯入檔案位置下方的 resources 位置。如您所見,開頭的斜線會被忽略。但是,鑑於這些路徑是相對的,最好不要完全使用斜線。根據 Spring Schema,被匯入檔案的內容(包括頂層 <beans/> 元素)必須是有效的 XML bean 定義。
|
可以使用相對 "../" 路徑參考父目錄中的檔案,但這不建議。這樣做會建立對當前應用程式外部檔案的相依性。特別是,不建議將此參考用於 您可以始終使用完全限定的資源位置而不是相對路徑:例如, |
命名空間本身提供了匯入指令功能。除了普通的 bean 定義之外,Spring 提供的一系列 XML 命名空間中還提供了更多組態功能,例如,context 和 util 命名空間。
Groovy Bean 定義 DSL
作為外部化組態中繼資料的另一個範例,bean 定義也可以在 Spring 的 Groovy Bean 定義 DSL 中表示,這從 Grails 框架中得知。通常,此類組態存在於 ".groovy" 檔案中,其結構如下列範例所示
beans {
dataSource(BasicDataSource) {
driverClassName = "org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"
url = "jdbc:hsqldb:mem:grailsDB"
username = "sa"
password = ""
settings = [mynew:"setting"]
}
sessionFactory(SessionFactory) {
dataSource = dataSource
}
myService(MyService) {
nestedBean = { AnotherBean bean ->
dataSource = dataSource
}
}
}這種組態樣式在很大程度上等同於 XML bean 定義,甚至支援 Spring 的 XML 組態命名空間。它也允許透過 importBeans 指令匯入 XML bean 定義檔案。
使用容器
ApplicationContext 是一個進階工廠的介面,能夠維護不同 bean 及其相依性的註冊表。透過使用方法 T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType),您可以檢索 bean 的實例。
ApplicationContext 讓您可以讀取 bean 定義並存取它們,如下列範例所示
-
Java
-
Kotlin
// create and configure beans
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
// retrieve configured instance
PetStoreService service = context.getBean("petStore", PetStoreService.class);
// use configured instance
List<String> userList = service.getUsernameList(); import org.springframework.beans.factory.getBean
// create and configure beans
val context = ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml")
// retrieve configured instance
val service = context.getBean<PetStoreService>("petStore")
// use configured instance
var userList = service.getUsernameList()使用 Groovy 組態,啟動看起來非常相似。它有一個不同的 Context 實作類別,它能識別 Groovy(但也理解 XML bean 定義)。以下範例顯示 Groovy 組態
-
Java
-
Kotlin
ApplicationContext context = new GenericGroovyApplicationContext("services.groovy", "daos.groovy");val context = GenericGroovyApplicationContext("services.groovy", "daos.groovy")最靈活的變體是 GenericApplicationContext 與讀取器委派結合,例如,使用 XmlBeanDefinitionReader 用於 XML 檔案,如下列範例所示
-
Java
-
Kotlin
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.xml", "daos.xml");
context.refresh();val context = GenericApplicationContext()
XmlBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.xml", "daos.xml")
context.refresh()您也可以將 GroovyBeanDefinitionReader 用於 Groovy 檔案,如下列範例所示
-
Java
-
Kotlin
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
new GroovyBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.groovy", "daos.groovy");
context.refresh();val context = GenericApplicationContext()
GroovyBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.groovy", "daos.groovy")
context.refresh()您可以在同一個 ApplicationContext 上混合和匹配此類讀取器委派,從不同的組態來源讀取 bean 定義。
然後,您可以使用 getBean 來檢索 bean 的實例。ApplicationContext 介面還有一些其他方法用於檢索 bean,但理想情況下,您的應用程式程式碼永遠不應使用它們。實際上,您的應用程式程式碼應該完全沒有對 getBean() 方法的呼叫,因此完全不依賴 Spring API。例如,Spring 與 Web 框架的整合為各種 Web 框架組件(例如控制器和 JSF 受管 bean)提供相依性注入,讓您可以透過中繼資料(例如自動裝配註解)宣告對特定 bean 的相依性。

